Expert System
Expert System

I read Luger’s book (Luger, 2021) on expert systems and discovered a way to model the CALM architecture using an expert system. This knowledge-based approach is essential for ongoing research involving expert systems.
Expert systems are a type of symbol-based AI grounded in rationalist presuppositions, inspired by the production system concept developed by Allen Newell and Herbert Simon. This production system framework also served as a foundation for expert system development.
The concept of the expert system was first proposed by Edward Feigenbaum and Joshua Lederberg in the 1960s. Feigenbaum conducted research at Stanford University, where he developed early expert systems such as MYCIN (a medical diagnosis system) and DENDRAL (a chemical structure analysis system). He is often referred to as the “Father of Expert Systems” and was awarded the ACM Turing Award in 1994.
Newell vs. Feigenbaum: Production System vs. Expert System
| Aspect | Newell & Simon (Production System) | Feigenbaum (Expert System) |
|---|---|---|
| Concept | A general reasoning model using if-then production rules. | AI that mimics human experts in a specific domain. |
| Goal | To develop a universal problem-solving framework. | To create AI that can reason like a human expert. |
| Key Contribution | Developed General Problem Solver (GPS) and SOAR [Newell & Simon, 1972]. | Developed DENDRAL (chemistry) and MYCIN (medicine) [Feigenbaum et al., 1971]. |
| Design Philosophy | Focused on symbolic reasoning and heuristic search [Newell, 1990]. | Focused on knowledge representation and rule-based inference [Feigenbaum, 1984]. |
| Scope | General-purpose AI applicable across domains. | Domain-specific AI specialized for expert tasks. |
| Influence | Inspired cognitive architectures like ACT-R and SOAR. | Led to the rise of expert systems in AI applications. |
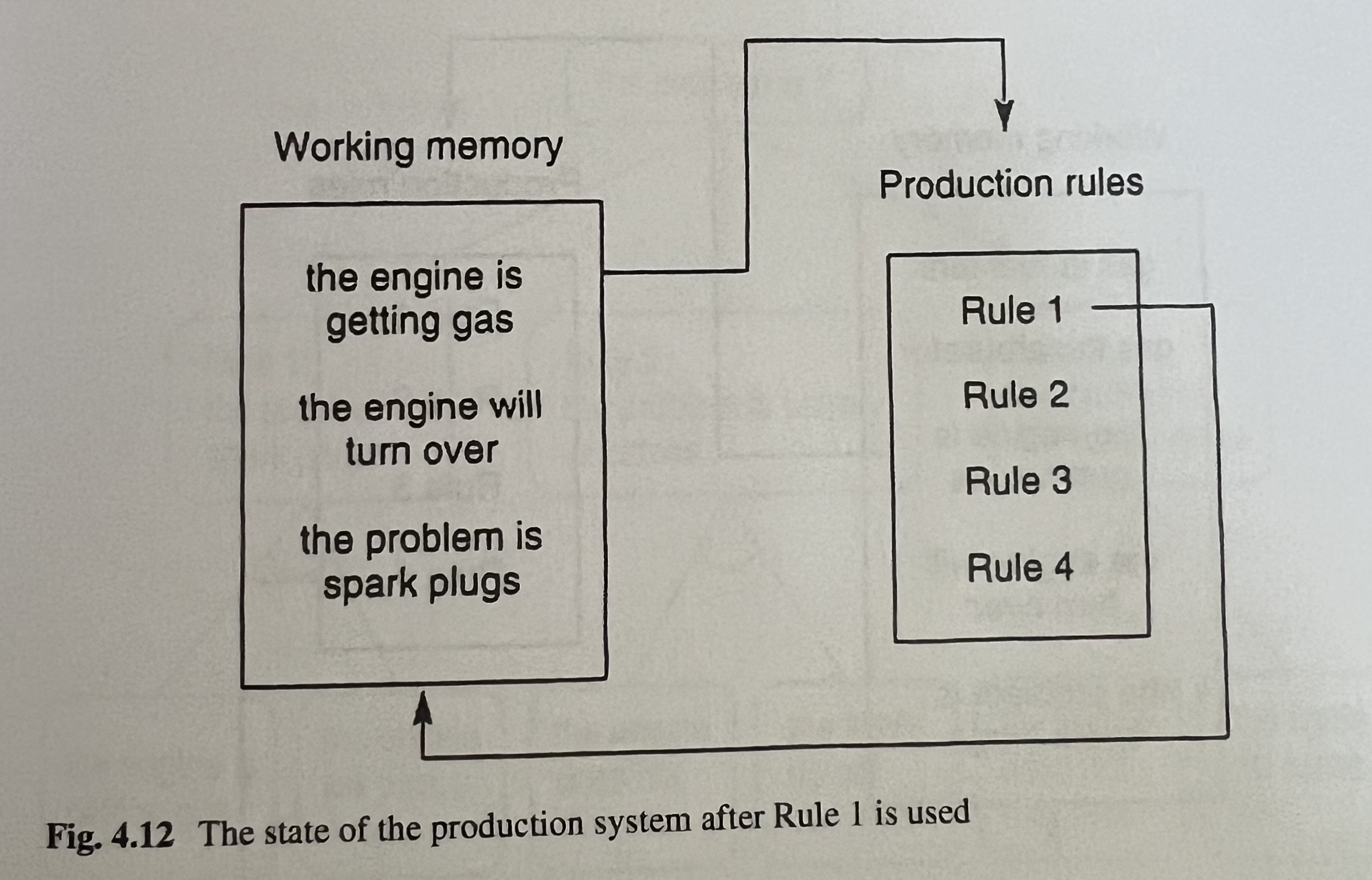
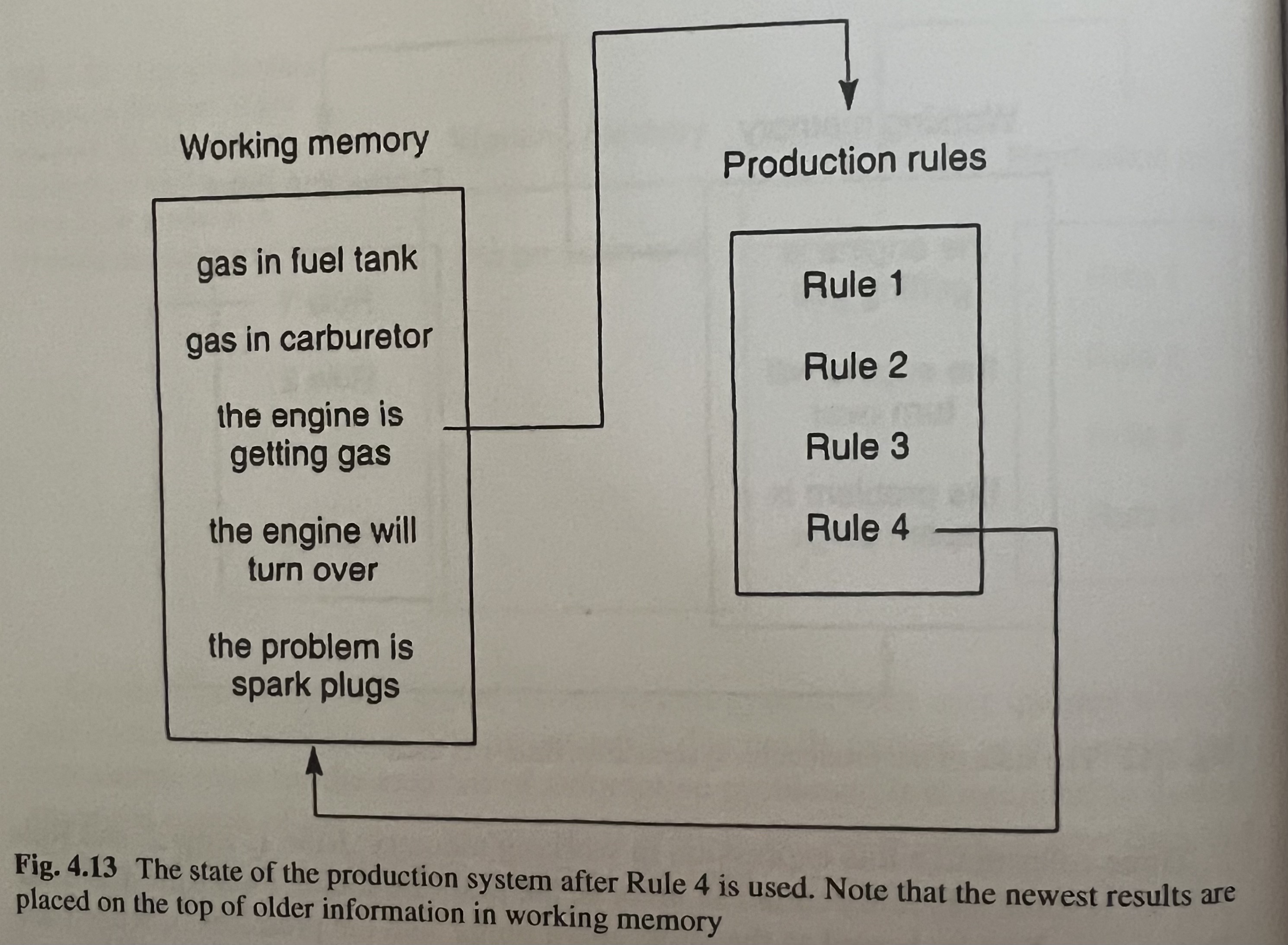
The implication of the system works simply by a restatement of the current rule under consideration and this offers answer for two types of questions:
- ex) engine will turn over:
- yes / no (This is a predicate type answering the state of the condition)
- why : This asks which rule is applied to the condition. (because of the rule A)
- how : This asks the reasoning process to the condition. The expected output is a set of rules executed to deduce the answer. (because of the rule A, with condition C and rule B with condition D)
List and Iterative Refinement Algorithm
While progressively applying rules and getting new memory. The list structure is used to store the memory. The Production rule (PR) can manage the working memory to remove and add memories to the list. I think it resembles the optimization process to find the necessary set for achieving purposes. In the case of human beings, they must survive considering the future and manage the necessary memories to effectively achieve the purpose. AI systems must follow the same philosophy to live in environments.
- RQ: What is the optimal size for an agent whose purposes is bounded? What is the optimal complexity of computational resources for the agent?
The necessary set is critical as the AI system can be predictable and controllable for the given purposes. This resembles the concept of topic Theory of the Size of a Calculation in the Dartmouth conference. They argued that
Some consideration will show that get a measure of the efficiency of a calculation, it is necessary to have on hand a method of measuring the complexity of calculating devices which in turn can be done if one has a theory of the complexity of functions.
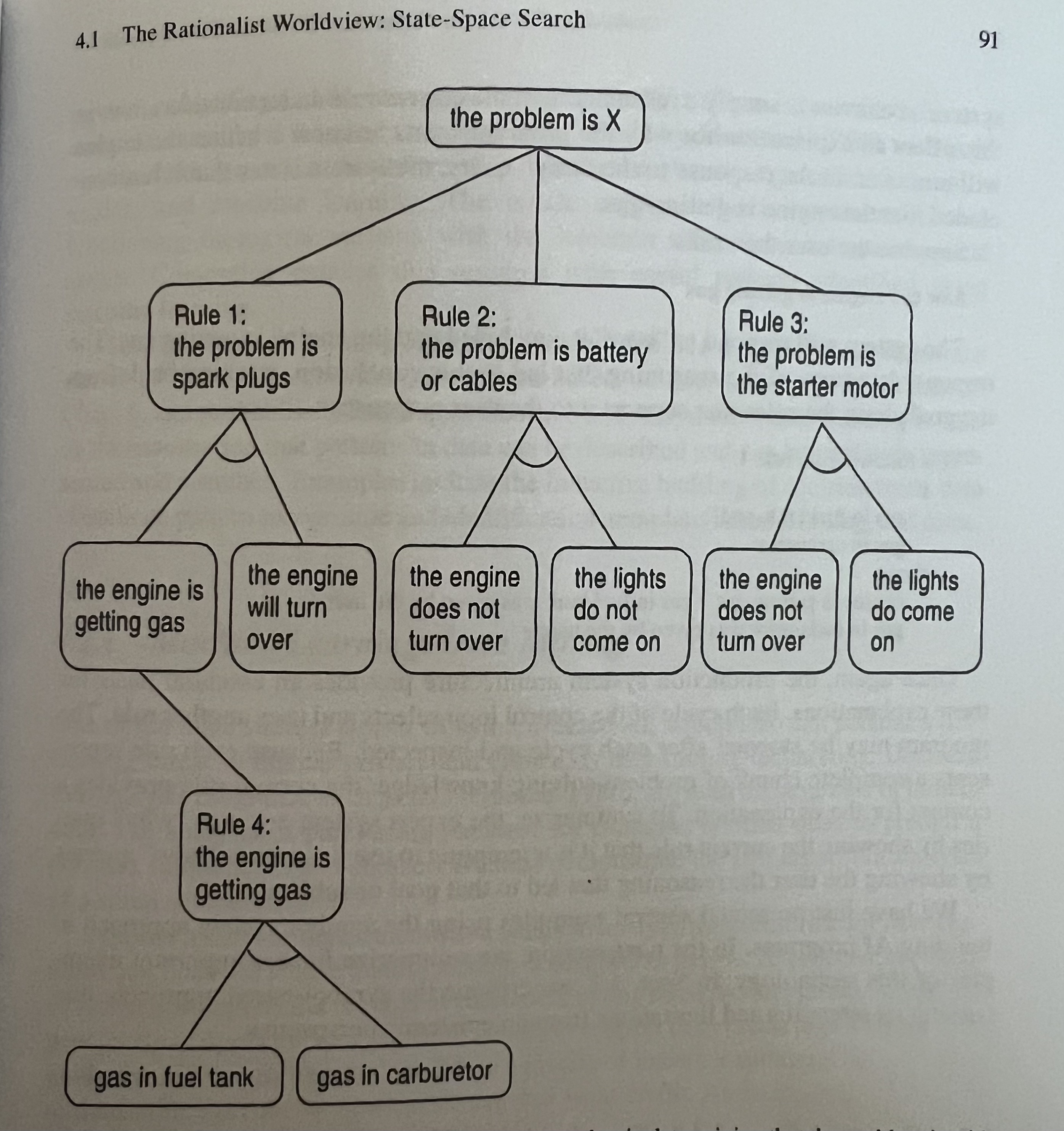
Search
GOFAI (Good Old Fashioned AI) is a search-based approach to solve the problem. The transparency of expert system provide state space of conditions, rules, and actions. Under the rationalist presuppositions (reason, logic, and innate knowledge), the search provide traversal of the state space. Meaning that we can expand the list format of working memory to find the necessary set.
References
- Newell, A., & Simon, H. A. (1972). Human Problem Solving. Prentice-Hall.
- Newell, A. (1990). Unified Theories of Cognition. Harvard University Press.
- Feigenbaum, E. A., Buchanan, B. G., & Lederberg, J. (1971). On Generality and Problem Solving: A Case Study Using the DENDRAL Program. Machine Intelligence, 6, 165–190.
- Feigenbaum, E. A. (1984). Knowledge Engineering: The Applied Side of Artificial Intelligence. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 426(1), 91–107.
- Luger, G. F. (2021). Knowing our world. Springer International Publishing AG.